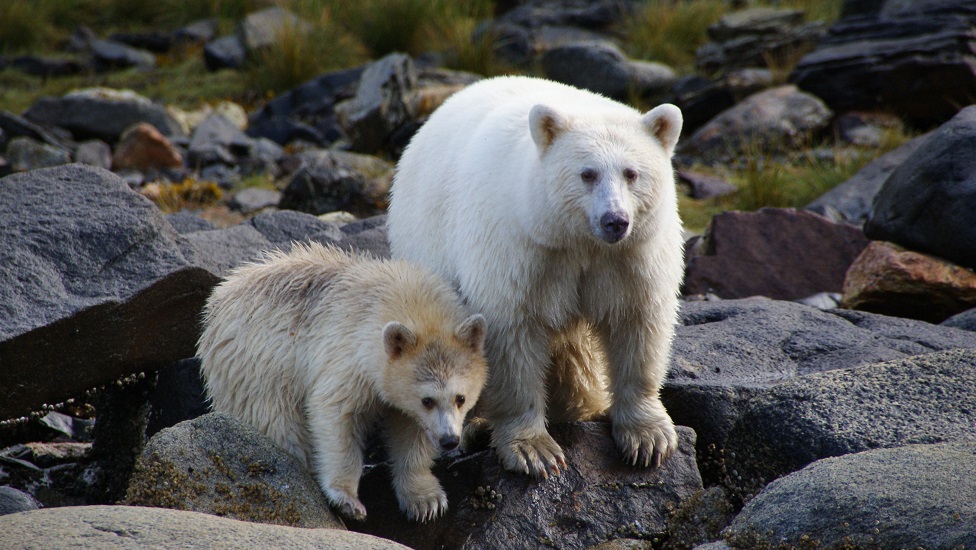
A genetics case study looking at the rare Kermode bear in BC
PURPOSE
In this short exercise sheet, students apply their knowledge of genetics and the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) to the rare, white Kermode bear in British Columbia. This activity is intended for advanced science classes and assumes that you have already covered the science of genetics and HWE.
GRADE LEVELS
12
TIME NEEDED
30 minutes

Curriculum LINKS
Biology 30, Unit D
MATERIALS NEEDED
Instructions
1: Review with your students the components of Population Genetics and the Hardy-Weinberg Principle.
The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium describes the relationship between allele frequencies and genotype frequencies under the assumption of random mating.
To maintain this equilibrium, a number of assumptions must be met:
- There must be no mutation
- There must be no migration
- Individuals must mate at random with respect to genotype
- There must be no selection
- The population must be infinitely large
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be expressed as:
p + q = 1 or p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
2: Have students complete the CSI Worksheet
Discussion
After reviewing the worksheet answers with the class, host a discussion on Spirit Bear conservation. Some questions could include:
- Should hunting of black bears in Spirit Bear Park be permitted?
- How does habitat loss and fragmentation impact Spirit Bear populations?
- What can you do to help protect this rare subspecies?
More Bring Nature Home for Teachers
Bring Nature Home is our online database of tried-and-tested CPAWS Southern Alberta activities! Here are some ways that you can bring nature home (or to the classroom) today!
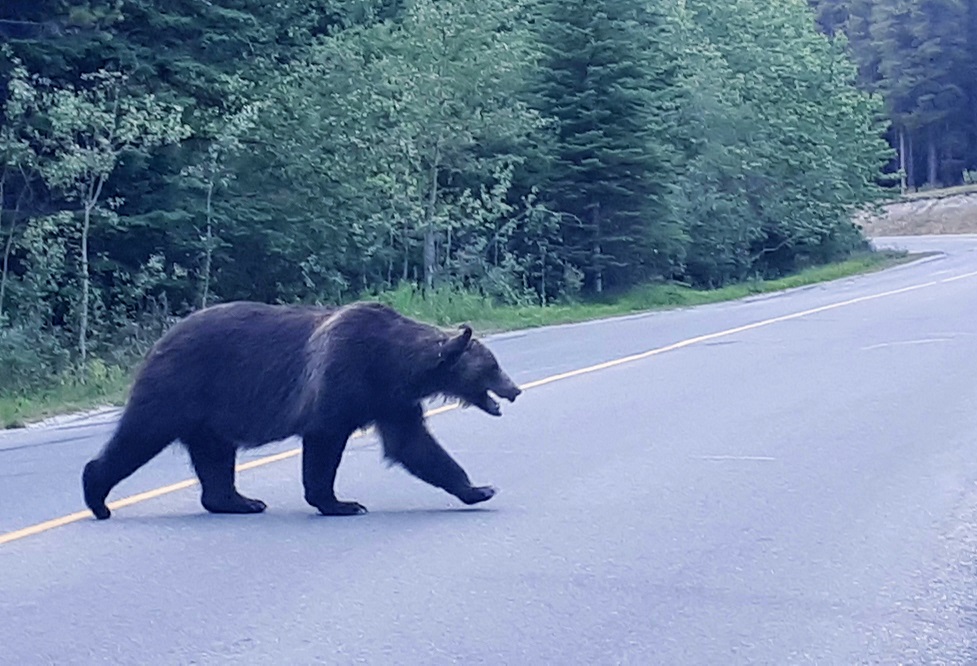

Habitat Effectiveness
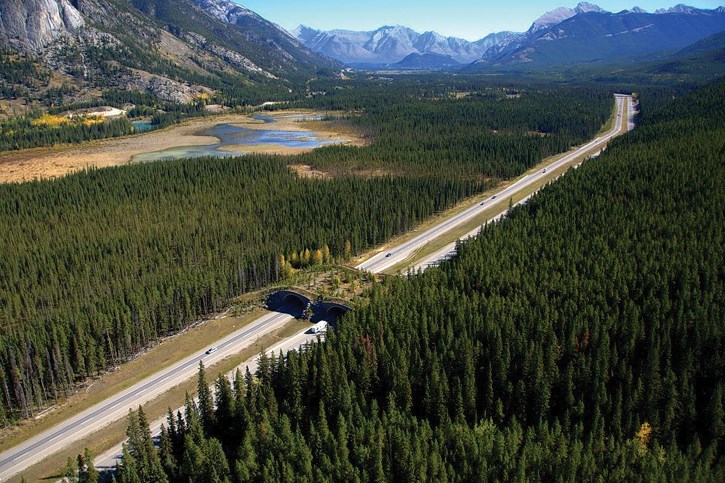

Room to Roam